Page 17 - Demo
P. 17
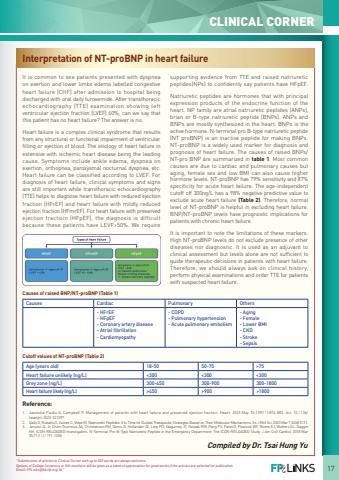
17CLINICAL CORNERInterpretation of NT-proBNP in heart failureIt is common to see patients presented with dyspnea on exertion and lower limbs edema labelled congestive heart failure (CHF) after admission to hospital being discharged with oral daily furosemide. After transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) examination showing left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 60%, can we say that this patient has no heart failure? The answer is no.Heart failure is a complex clinical syndrome that results from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood. The etiology of heart failure in extensive with ischemic heart disease being the leading cause. Symptoms include ankle edema, dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, etc. Heart failure can be classified according to LVEF. For diagnosis of heart failure, clinical symptoms and signs are still important while transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) helps to diagnose heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and heart failure with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF). For heart failure with preserved ejection fractioin (HFpEF), the diagnosis is difficult because these patients have LEVF>50%. We require supporting evidence from TTE and raised natriuretic peptides(NPs) to confidently say patients have HFpEF. Natriuretic peptides are hormones that with principal expression products of the endocrine function of the heart. NP family are atrial natriuretic peptides (ANPs), brian or B-type natriuretic peptide (BNPs). ANPs and BNPs are mostly synthesized in the heart. BNPs is the active hormone. N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT proBNP) is an inactive peptide for making BNPs. NT-proBNP is a widely used marker for diagnosis and prognosis of heart failure. The causes of raised BNPs/ NT-pro BNP are summarized in table 1. Most common causes are due to cardiac and pulmonary causes but aging, female sex and low BMI can also cause higher hormone levels. NT-proBNP has 79% sensitivity and 87% specificity for acute heart failure. The age-independent cutoff off 300ng/L has a 98% negative predictive value to exclude acute heart failure (Table 2). Therefore, normal level of NT-proBNP is helpful in excluding heart failure. BNP/NT-proBNP levels have prognostic implications for patients with chronic heart failure.It is important to note the limitations of these markers. High NT-proBNP levels do not exclude presence of other diseases nor diagnostic. It is used as an adjuvant to clinical assessment but levels alone are not sufficient to guide therapeutic decisions in patients with heart failure. Therefore, we should always ask on clinical history, perform physical examinations and order TTE for patients with suspected heart failure.%u201cSubmissions of articles to Clinical Corner with up to 500 words are always welcome. Options of College Souvenirs or Gift vouchers will be given as a token of appreciation for good works if the articles are selected for publication. Email: FPLinks@hkcfp.org.hk%u201dCompiled by Dr. Tsai Hung YuReference:1.Jasinska-Piadlo A, Campbell P. Management of patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. Heart. 2023 May 15;109(11):874-883. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2022-321097. 2.Gallo G, Rubattu S, Autore C, Volpe M. Natriuretic Peptides: It Is Time for Guided Therapeutic Strategies Based on Their Molecular Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 7;24(6):5131. 3.Januzzi JL Jr, Chen-Tournoux AA, Christenson RH, Doros G, Hollander JE, Levy PD, Nagurney JT, Nowak RM, Pang PS, Patel D, Peacock WF, Rivers EJ, Walters EL, Gaggin HK; ICON-RELOADED Investigators. N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in the Emergency Department: The ICON-RELOADED Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Mar 20;71(11):1191-1200.Age (years old)18-5050-75>75Heart failure unlikely (ng/L)<300<300<300Grey zone (ng/L)300-450300-900300-1800Heart failure likely (ng/L)>450>900>1800CausesCardiacPulmonaryOthers-HFrEF-HFpEF-Coronary artery disease-Atrial fibrillation-Cardiomyopathy-COPD-Pulmonary hypertension-Acute pulmonary embolism-Aging-Female-Lower BMI-CKD-Stroke-SepsisCutoff values of NT-proBNP (Table 2)Causes of raised BNP/NT-proBNP (Table 1)