Table 2: The prescription pattern of first-line antihypertensive agents among basic and higher trainees in patients presented with hyperlipidemia (no./%)
| Basic trainees (n=76) | Higher trainees* (n=25) | |||||||||
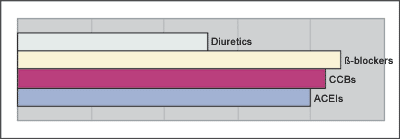
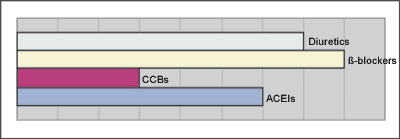
| Q5 (A) Young Male | ||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||
| Diuretics | 13 | (17.1%) | 7 | (28.0%) | ||||||
| 22 | (28.9%) | 8 | (32.0%) | |||||||
| CCBs | 21 | (27.6%) | 3 | (12.0%) | ||||||
| ACEIs | 20 | (26.3%) | 6 | (24.0%) | ||||||
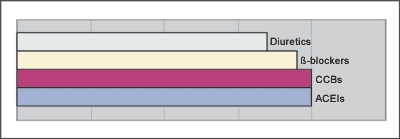
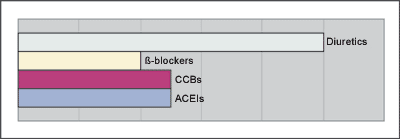
| Q5 (B) Elderly Male | ||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||
| Diuretics | 17 | (22.4%) | 10 | (40.0%) | ||||||
| 19 | (25.0%) | 4 | (16.0%) | |||||||
| CCBs | 20 | (26.3%) | 5 | (20.0%) | ||||||
| ACEIs | 20 | (26.3%) | 5 | (20.0%) | ||||||
| Q6 (A) Young Female | ||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||
| Diuretics | 13 | (17.1%) | 7 | (28.0%) | ||||||
| 22 | (28.9%) | 8 | (32.0%) | |||||||
| CCBs | 21 | (27.6%) | 3 | (12.0%) | ||||||
| ACEIs | 20 | (26.3%) | 6 | (24.0%) | ||||||
| Q6 (B) Elderly Female | ||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||
| Diuretics | 17 | (22.4%) | 10 | (40.0%) | ||||||
| 19 | (25.0%) | 4 | (16.0%) | |||||||
| CCBs | 20 | (26.3%) | 5 | (20.0%) | ||||||
| ACEIs | 20 | (26.3%) | 5 | (20.0%) | ||||||
| (*Not included was one higher trainee who chose agents other than the specified groups, namely Candesartan Cilexetil (Blopress) and Losartan and hydrochlorothiazide (Hyzaar) for the male and female gender groups respectively, disregarding patient age) | ||||||||||